emDOCs Podcast – Episode 110: Primary Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
EMDocs
NOVEMBER 13, 2024
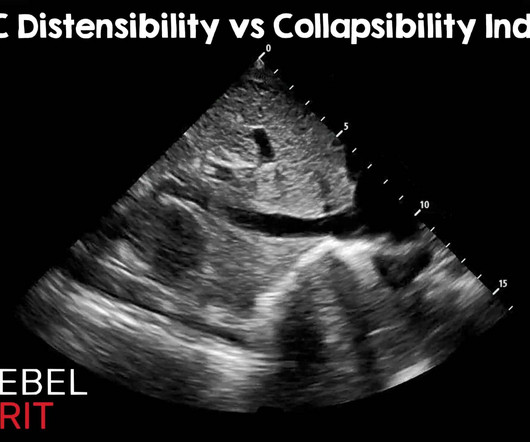
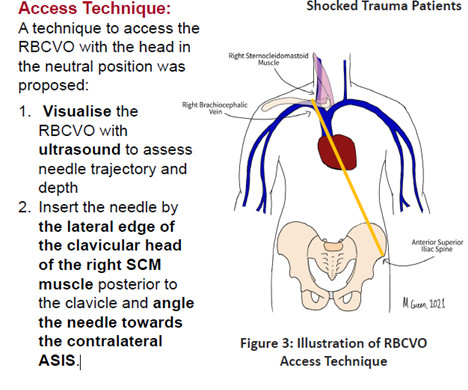
Ultrasound can assist: confirm ascites, evaluate for best site, abdominal wall thickness, blood vessels along needle track. Management: Patients can rapidly progress to septic shock and multiorgan failure. Safety of ultrasound-guided thoracentesis in patients with abnormal preprocedural coagulation parameters. 2013;144:456–463.










































Let's personalize your content