Targeted Temperature Management in Paediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Don't Forget the Bubbles
NOVEMBER 11, 2024
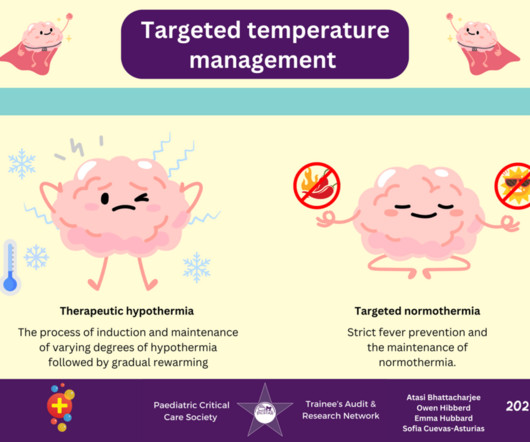
Therapeutic hypothermia is thought to decrease the brain’s metabolic demand, reduce inflammation and cell death, and reduce the risk of seizures. The aim of TTM is to control the body and brain’s temperature, thus reducing secondary brain injury and improving the neurological outcome. What do the guidelines recommend?
















































Let's personalize your content