"Sepsis bundles": No good evidence of benefit
PulmCCM
APRIL 14, 2025
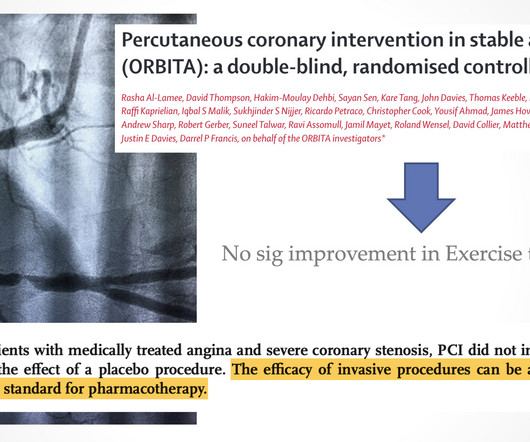
SEP-1 was pushed through without waiting for the outcomes of three ongoing multicenter trials testing goal-directed therapy for sepsis. But not completely prohibited: CMS has the authority to grant exceptions to SEP-1 reporting for the purposes of research. Ann Intern Med. 2025 Feb 18. doi: 10.7326/ANNALS-24-02426. Epub ahead of print.










































Let's personalize your content