Sepsis Screening Decreases Mortality. Well, not really.
Sensible Medicine
MARCH 14, 2025
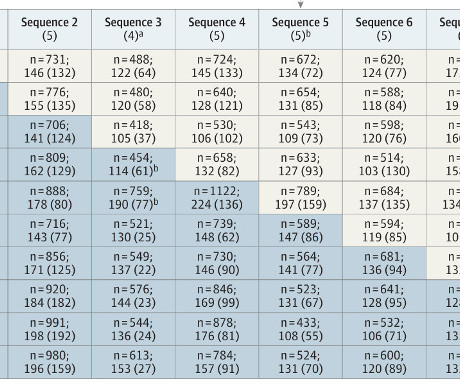
This comment might be one of the reasons I’ve been skeptical of sepsis screening. Sepsis screening, for me, comes in many different flavors -- from EMR alerts based on lab and vital sign data to anyone being able to draw a lactate or call an RRT. Outcomes and patients The primary outcome was 90-day in-hospital mortality.












































Let's personalize your content