Dysphagia and Cervical Spine Injury
The Trauma Pro
JULY 9, 2024
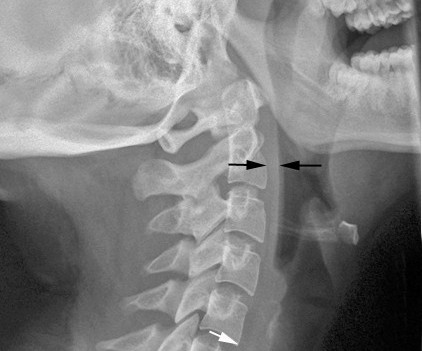
Patients with cervical fractures more commonly need a tracheostomy for ventilatory support and/or have a head injury , and these are well known culprits in dysphagia Normal soft tissue (<6mm at C2, <22mm at C6) A study in the Jan 2011 Journal of Trauma outlined the dysphagia problem seen with placement of a halo vest.












































Let's personalize your content