Sepsis Screening Decreases Mortality. Well, not really.
Sensible Medicine
MARCH 14, 2025
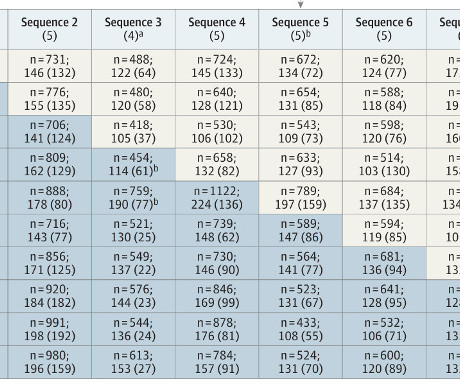
If sepsis screening was shown to be beneficial in one hospital, would it be beneficial in another, with an entirely different set of caregivers? Article Background With all that as background, I was excited when I saw the article Electronic Sepsis Screening Among Patients Admitted to Hospital Wards in JAMA.















































Let's personalize your content