ECG Blog #436 — Bigeminy or Alternans?
Ken Grauer, MD
JUNE 27, 2024
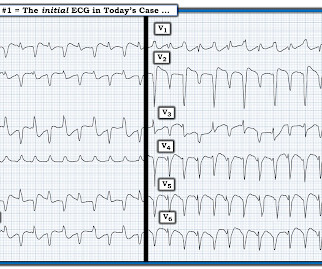
The ECG in Figure-1 — was obtained from an older man with known coronary disease. He developed cardiac arrest shortly after the ECG in Figure-1 was recorded. QUESTIONS: How would YOU interpret the ECG in Figure-1 ? QUESTIONS: How would YOU interpret the ECG in Figure-1 ? Figure-1: The initial ECG in today's case. (






















Let's personalize your content