Seizure in a 30 something
Dr. Smith's ECG Blog
SEPTEMBER 2, 2024
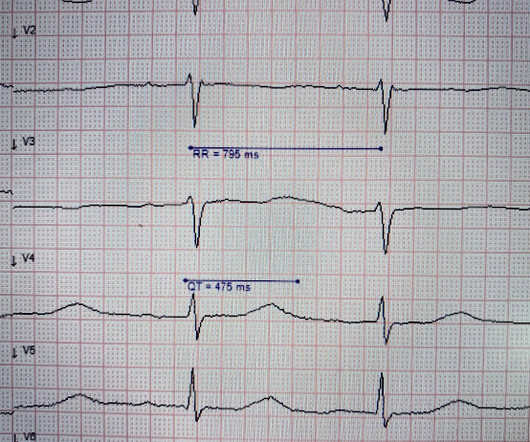
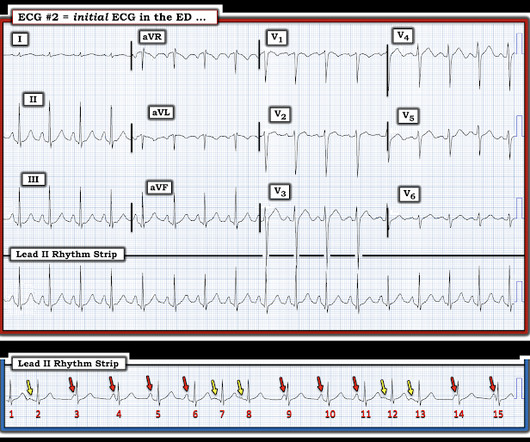
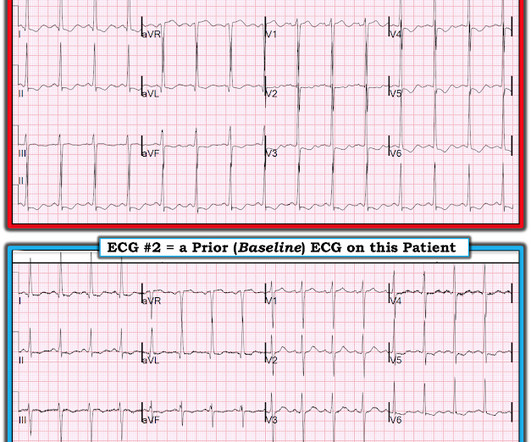
Her husband called EMS when the patient experienced new onset seizures accompanied by micturition. The ECG below was recorded by EMS. ECG #1 Interpretation: ECG #1 shows sinus rhythm at a heart rate of 77 bpm. At first glance, the ECG does not look too abnormal. All patients with seizures needs an ECG.















Let's personalize your content