Sudden shock with a Nasty looking ECG. What is it?
Dr. Smith's ECG Blog
MAY 3, 2024
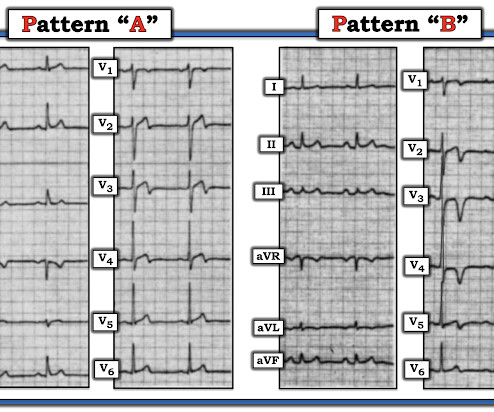
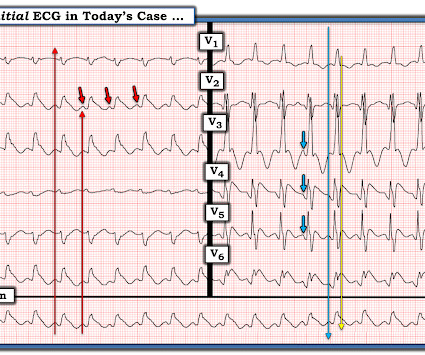
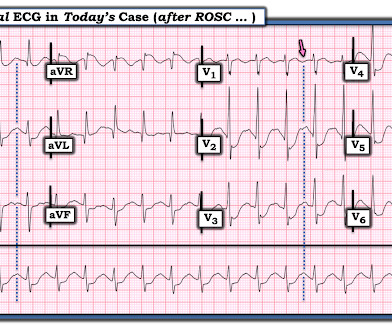
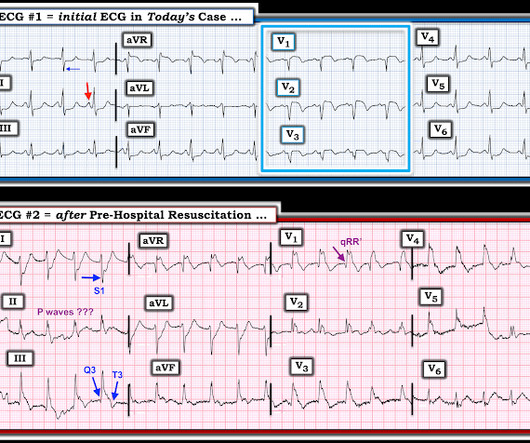
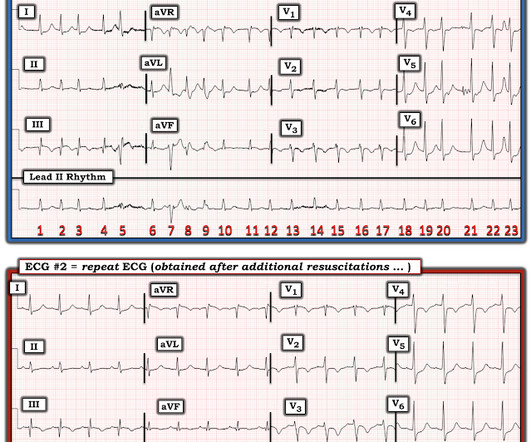
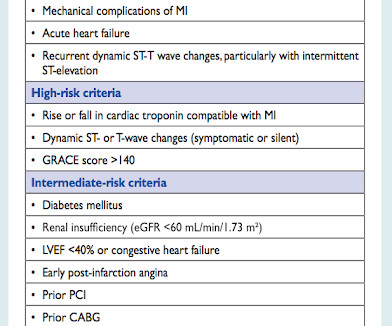
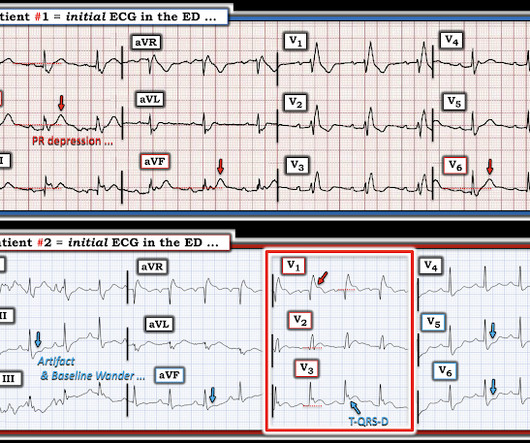
She was found by medics agitated, hypotensive, diaphoretic, and in shock. There were 2 prehospital ECGs: What do you think? When I was shown this ECG, I said it looks like such widespread ischemia that is might be a left main occlusion, or LM ischemia plus circumflex occlusion (high lateral and posterior OMI).







































Let's personalize your content