ToxCard: Second Generation Antipsychotic Overdose
EMDocs
NOVEMBER 19, 2024
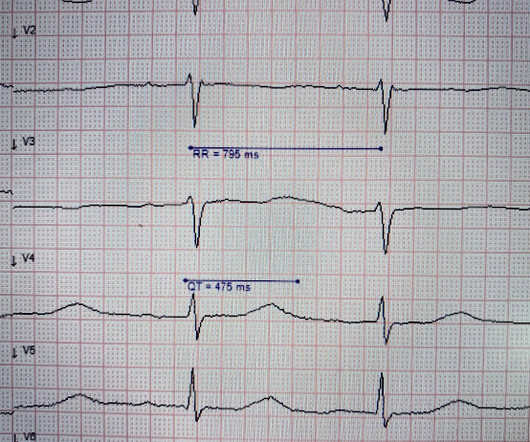
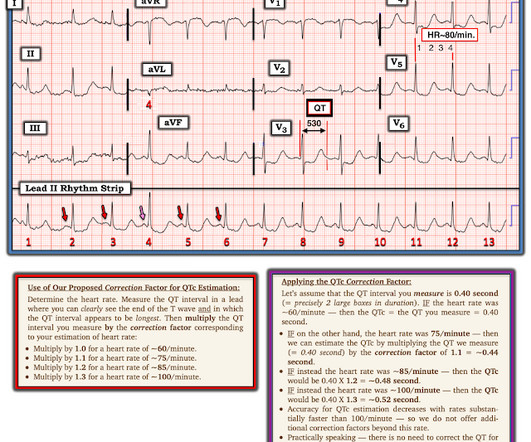
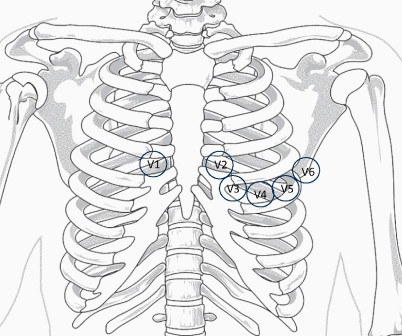
1 Seizures may occur due to lowered seizure threshold. 6 Seizures have been observed and are dose-dependent. Recommend obtaining multiple EKGs to aid in the diagnosis of cardiotoxic effects such as dysrhythmias or interval widening, even if not apparent immediately after the overdose. 8 Hypersalivation can occur.




































Let's personalize your content