ECG Blog #435 — Did Cath Show Acute Ischemia?
Ken Grauer, MD
JUNE 22, 2024
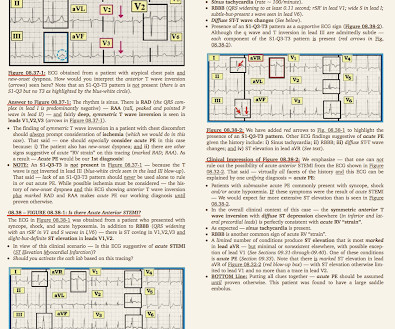
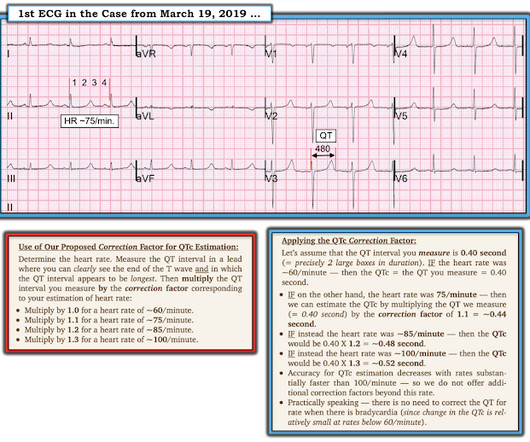
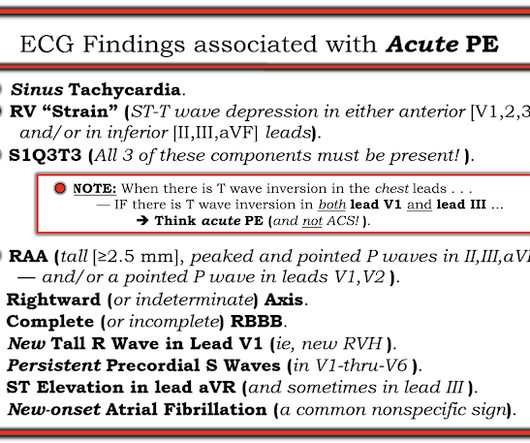
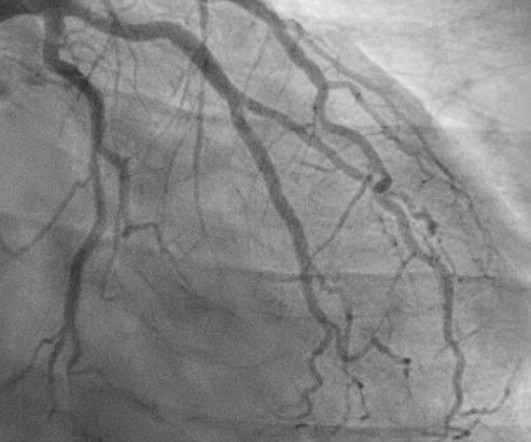
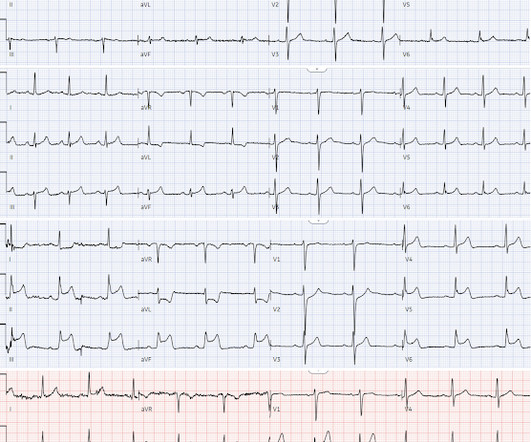
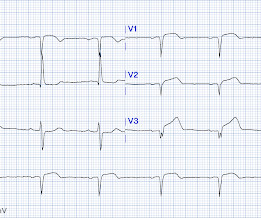
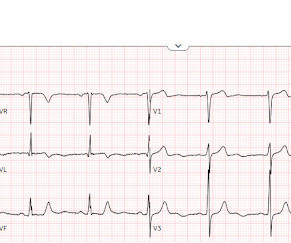
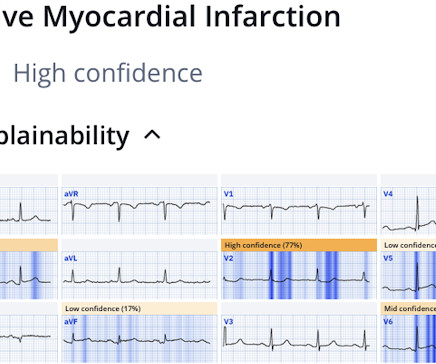
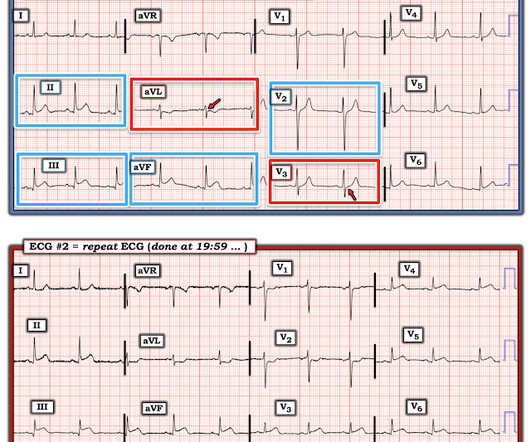
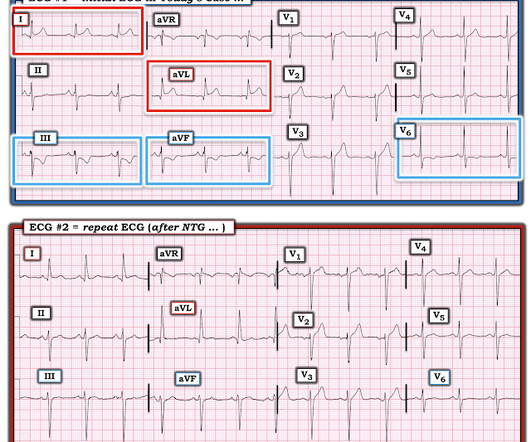
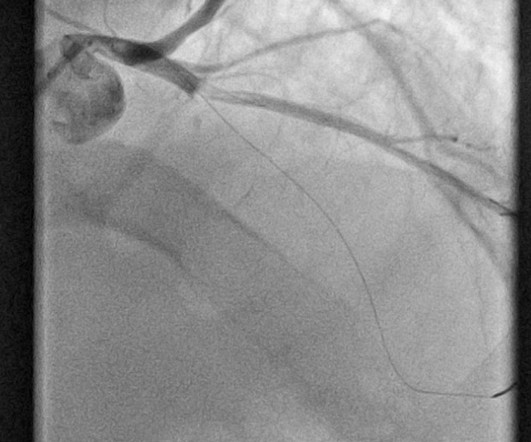
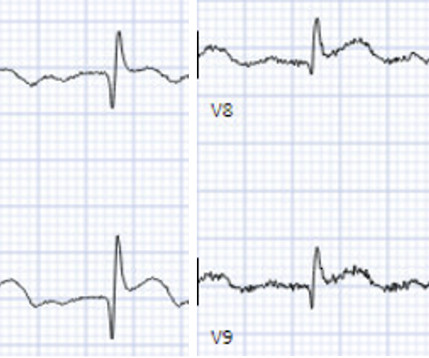
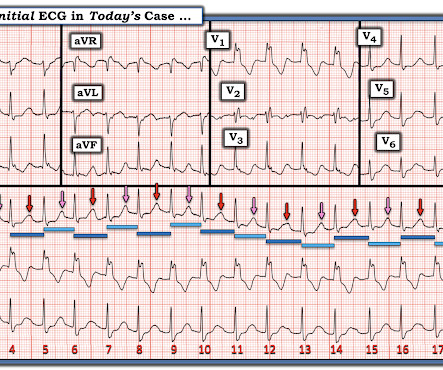
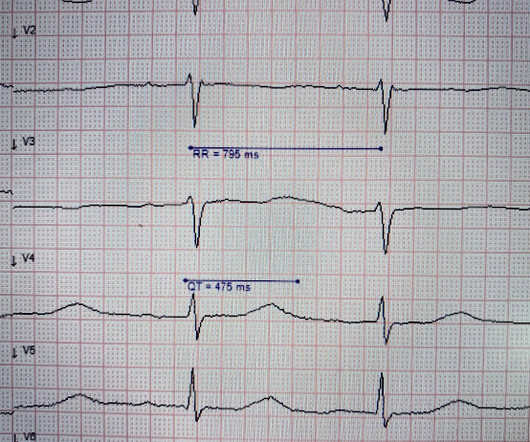
The ECG in Figure-1 — was obtained from a middle-aged woman with positional tachycardia and diaphoresis with change of position from suprine to sitting. Although CP ( C hest P ain ) was not a prominent symptom — ACS ( A cute C oronary S yndrome ) was suspected from the chest lead T wave inversion seen on this ECG. WHY — or Why Not?



































Let's personalize your content