emDOCs Podcast – Episode 98: Post ROSC Mental Model
EMDocs
APRIL 2, 2024
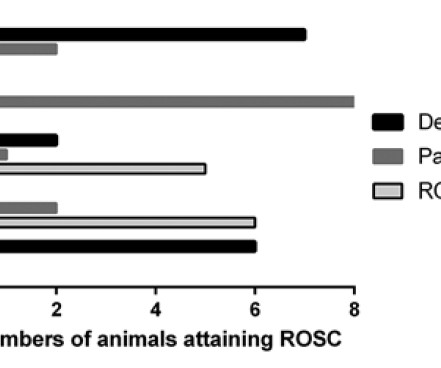
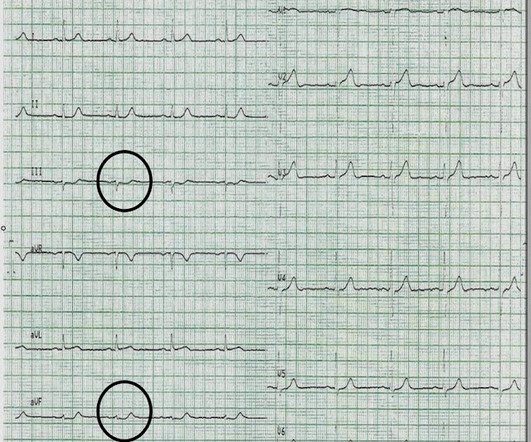
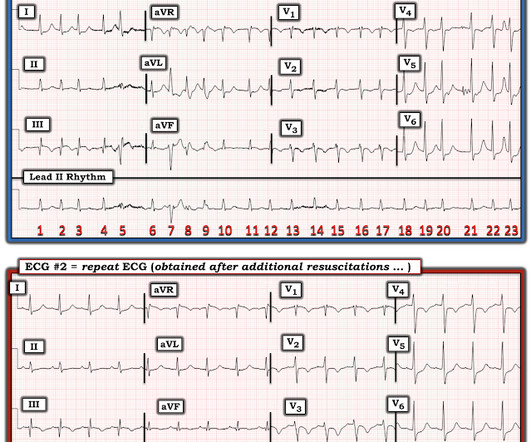
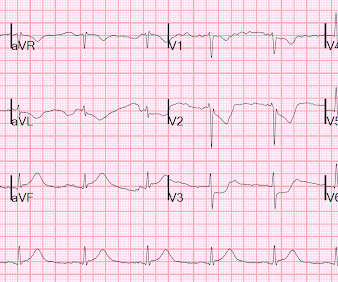
Check the pulse RSI= Resuscitation Sequence Intubation Hypoxia, Hypotension, and Acidosis are the reason patients code during/post intubation These patients are super high risk for all 4 Optimize first pass success – Induction agent + paralytic Unconscious patients will still have muscle tone Induction Ketamine or Etomidate at half doses (i.e.,



























Let's personalize your content