Improving the qualities of ventilations during CPR
Emergency Live
MAY 14, 2024
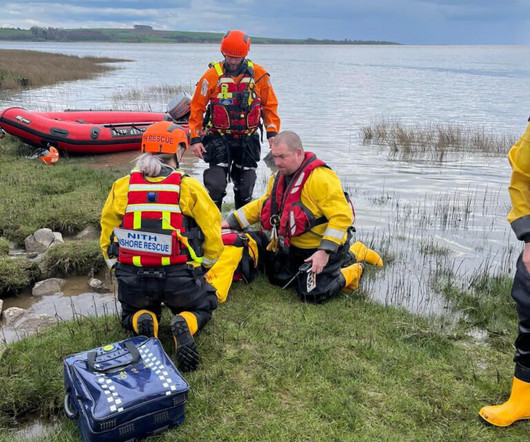
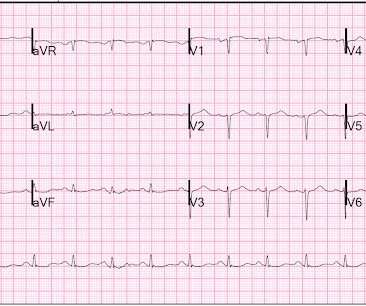
The ventilation maneuver during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a complex intervention influenced by various factors related to the patient, the operator, and the environment.











































Let's personalize your content