Ultrasound in Cardiac Arrest
Mount Sinai EM
AUGUST 7, 2024
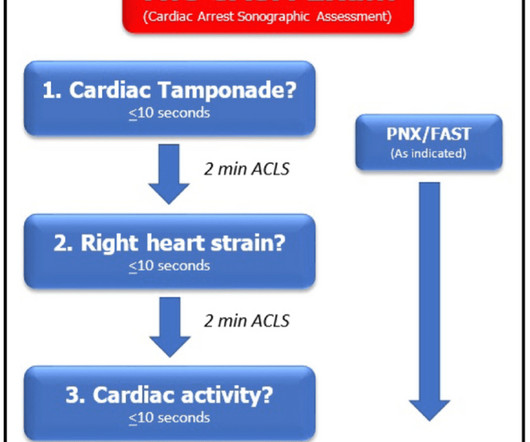
Ultrasound during cardiac arrest has quickly become standard. Initially, data suggested that the use of ultrasound during arrest increased pauses between compressions which worsens outcomes. The ideal view depends on the patient’s comorbid conditions such as COPD, obesity, cachexia, etc.















Let's personalize your content