Tools you should use: Pediatric NIH Stroke Scale
PEMBlog
APRIL 24, 2024
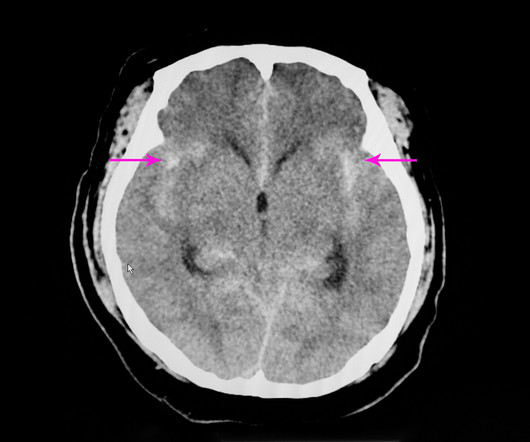
Pediatric strokes are rare and challenging to diagnose. There is a validated Pediatric Stroke Scale from the NIH that can be used in conjunction with a stroke protocol that involves Neurology, Radiology, and a local/regional Stroke Team. Early consultation with a pediatric hematologist and neurologist is mandatory.

























Let's personalize your content