Awake, and Paralysed: A Never Event
Don't Forget the Bubbles
NOVEMBER 29, 2023
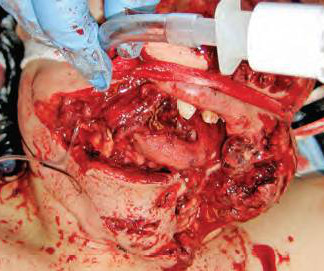
Ben has a possible skull fracture and has been intubated, but his oxygen requirement is minimal. Awake fiberoptic intubation where the patient consents, co-operative AND the airway is prepared with local anaesthesia. Key take-home points While Ben’s case is tragic, we can learn important points about airway management.










Let's personalize your content