Trauma Resuscitation Updates
RebelEM
MAY 25, 2023
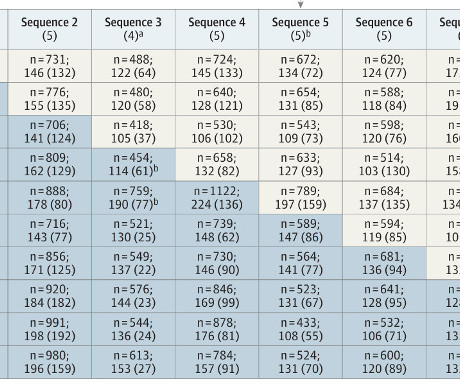
CRYSTALLOIDS Too much crystalloid resuscitation in traumatic hemorrhagic shock can increase dilutional coagulopathy, as well as increase morbidity and mortality Bickell WH et al. I recently gave a talk on the initial management of trauma patients with hemorrhagic shock. vs SBP target <90mmHg which resulted in a mortality of 33.4%

































Let's personalize your content