Sepsis Screening Decreases Mortality. Well, not really.
Sensible Medicine
MARCH 14, 2025
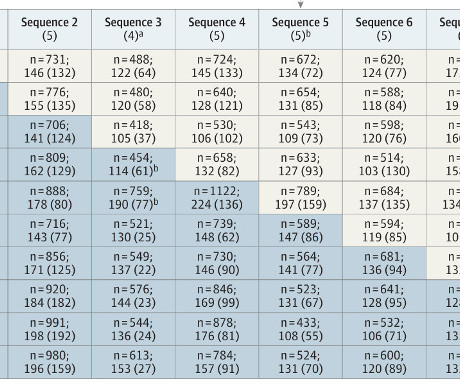
The only problem was that the patient population would change over the course of the study – the unscreened population was studied mostly in 2019 and early 2020 while the screened population was mostly late 2020 early 2021. Outcomes and patients The primary outcome was 90-day in-hospital mortality. Now to the journal.

























Let's personalize your content