Is the blind Subclavian “trauma line” a thing of the past?
Greater Sydney Area HEMS
FEBRUARY 20, 2024
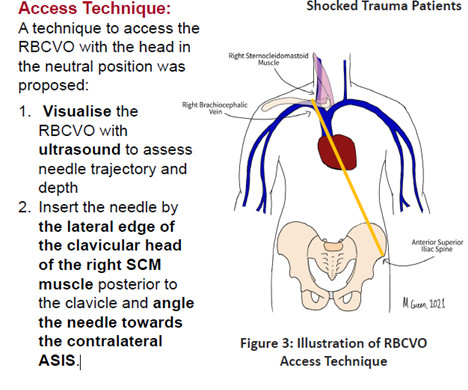
Obtaining access in shocked trauma patients can be notoriously difficult due to circulatory collapse. Those who are shocked, shut down with limited or no other options for peripheral access require central access. The evidence for improved safety and quality with the use of ultrasound for CVC implementation is well established [i].





































Let's personalize your content