Neurogenic Shock in Children
Pediatric EM Morsels
SEPTEMBER 22, 2023
Physical exam findings of occult shock in children can be subtle. Fortunately, there are screening tools for occult shock. A (sorta) Quick Blurb about Spinal Shock If you, like me, have recently had to go back to review the difference between spinal and neurogenic shock , here is a quick refresher on the topic.




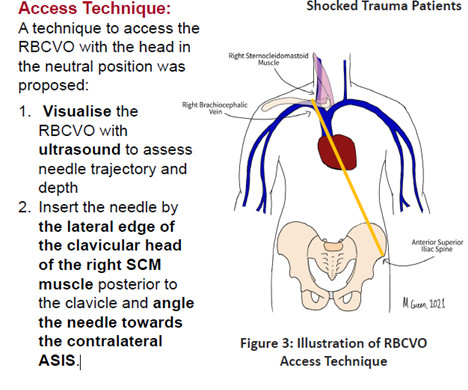









































Let's personalize your content