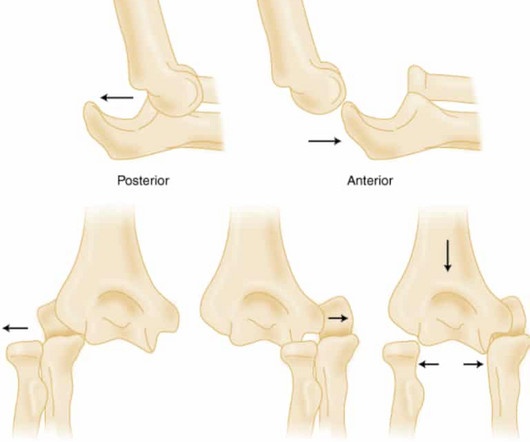
Elbow Dislocations
RebelEM
NOVEMBER 6, 2024
2017 Jul;9(3):195-204. Elbow Dislocations in the Emergency Department: A Review of Reduction Techniques. J Emerg Med. Commentary on an article by Marc Schnetzke, MD, et al.: “Determination of Elbow Laxity in a Sequential Soft-Tissue Injury Model. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Shoulder Elbow.










Let's personalize your content