US Probe: Suprapatellar Recess Injection for Chronic Knee Pain in the Emergency Department – An Effective Approach for Relief
EMDocs
APRIL 7, 2025
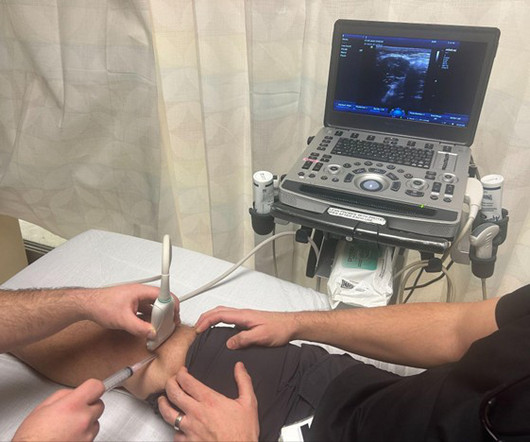
Author: Abdo Zeinoun MD, Clinical Ultrasound Fellow, Department of Emergency Medicine, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School // Reviewed by: Stephen Alerhand, MD ( @SAlerhand) ; Steve Fields, MD Patient Case A 60 year-old male with a history of hypertension presents with worsening right knee pain over the last 3 days. Why Use Ultrasound Guidance?











Let's personalize your content