Elbow Dislocations
RebelEM
NOVEMBER 6, 2024
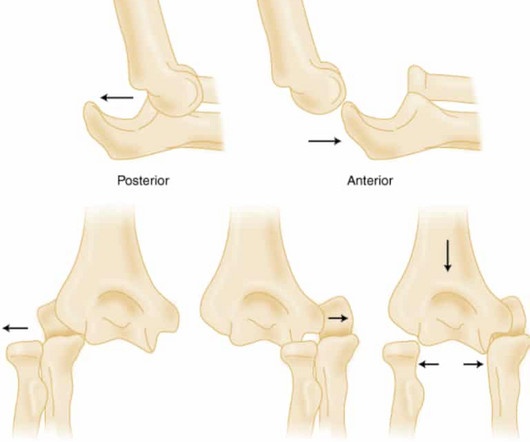
Commentary on an article by Marc Schnetzke, MD, et al.: “Determination of Elbow Laxity in a Sequential Soft-Tissue Injury Model. 2015 Jan;38(1):42-4. PMID: 28846302 O’Driscoll SW. How Do Elbows Dislocate?: A Cadaveric Study” J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018 Apr 4;100(7):e46. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.17.01448.












Let's personalize your content