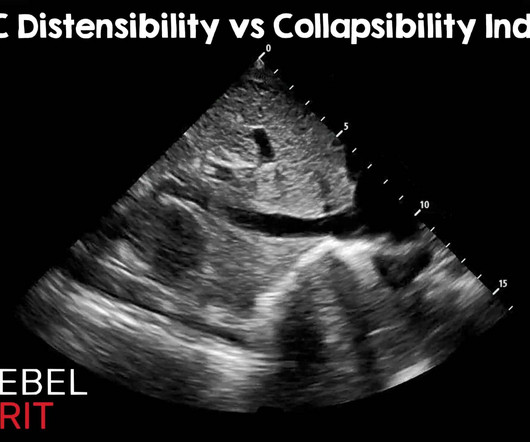
IVC Distensibility Index vs Collapsibility Index: Using the Correct Index
RebelEM
FEBRUARY 24, 2025
19 These are all invaluable tools that providers can use at the bedside to assess the probability of a patient responding to IV fluids. Regarding caval indexes, the advent of artificial intelligence and advanced learning has become integrated into many ultrasound machines. Ultrasound Med Biol. May 2014; PMID: 24495437.













Let's personalize your content