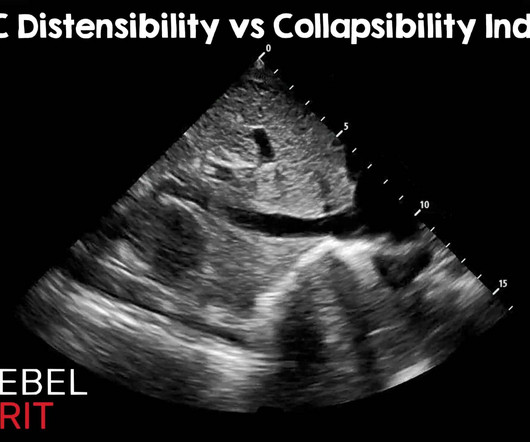
IVC Distensibility Index vs Collapsibility Index: Using the Correct Index
RebelEM
FEBRUARY 24, 2025
13 That is to say nothing of the effect that the type and response to shock has on the individual patients involved in these studies. As seen in the Andromeda Shock Trial, and multiple other trials involving shocked patients, capillary return also reigns supreme regarding physical examination. Mar 2004; PMID: 15090949.























Let's personalize your content