ACMT Toxicology Visual Pearl: Salt, not Shock
ALiEM
FEBRUARY 20, 2024
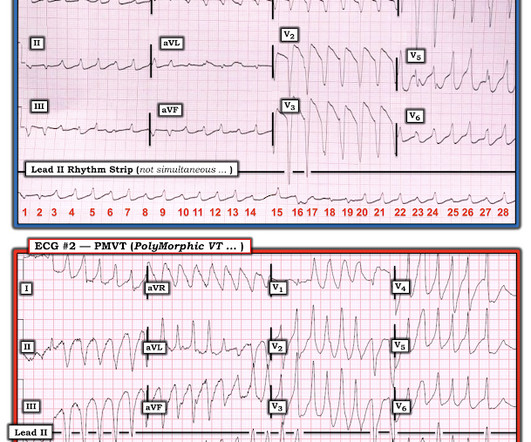
What agent would most likely be responsible for these ECG findings? This EKG shows a wide complex (QRS 240 msec), irregular rhythm with left bundle branch block morphology at a rate slower than expected (90 bpm) for a ventricular arrhythmia such as ventricular tachycardia. 2013 Dec;15(4):90-2. Epub 2013 Nov 7.
























Let's personalize your content