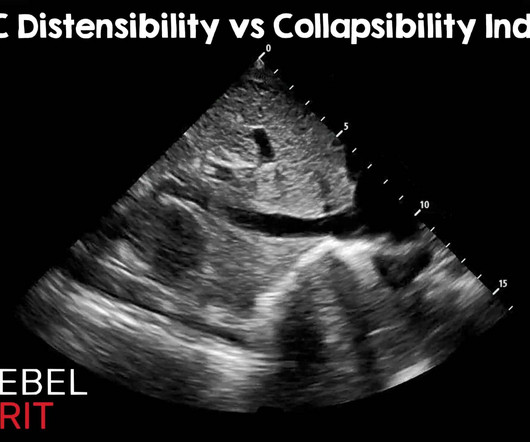
IVC Distensibility Index vs Collapsibility Index: Using the Correct Index
RebelEM
FEBRUARY 24, 2025
Well, the established cutoff for the distensibility index is 18%. 13 That is to say nothing of the effect that the type and response to shock has on the individual patients involved in these studies. Oct 2012; PMID: 23043910 Kumar A, et al. Why does it matter? 17 Of course, do not forget your physical exam. Castro R, et al.













































Let's personalize your content