Elbow Dislocations
RebelEM
NOVEMBER 6, 2024
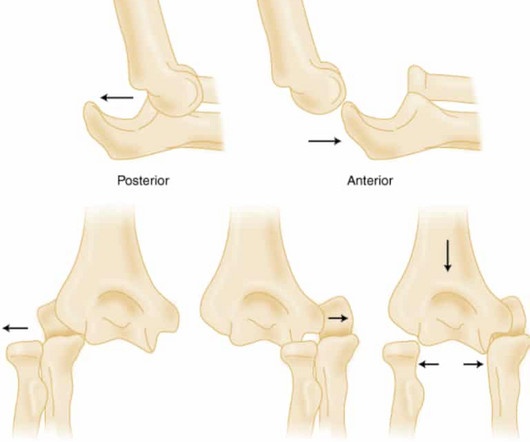
Elbow Dislocation Definition: Disarticulation of the proximal radius & ulna bones from the humerus Epidemiology: Incidence Second most common joint dislocation (after shoulder) in adults Most commonly dislocated joint in children Accounts for 10-25% of all injuries to the elbow ( Cohen 1998 ) Posterolateral is the most common type of dislocation (..)










Let's personalize your content