The 90th Bubble wrap DFTB X The Bridge
Don't Forget the Bubbles
MARCH 31, 2025
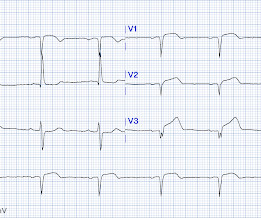
Sepsis is a significant cause of mortality in children, and fluid resuscitation is a key treatment strategy. It also emphasizes the need for better fluid management strategies, including early de-resuscitation in high-risk patients. 41% of patients with septic shock had MODS. Why does it matter? Am J Emerg Med. 2025.01.054.




























Let's personalize your content