Chest Pain in Children: ReBaked Morsel
Pediatric EM Morsels
MAY 10, 2024
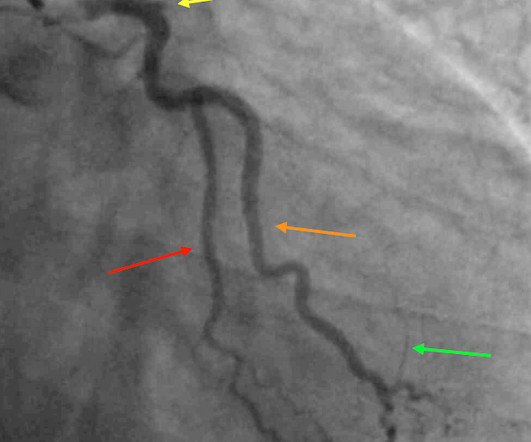
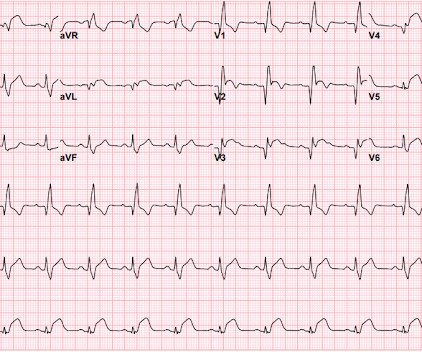
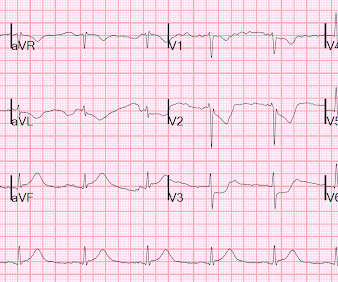
EKG Reasonable screen for cardiac etiology [ Kane, 2010 ]: Chest Pain with Exertion? Ultrasound diagnosis of occult pneumothorax. 2005 Jun;33(6):1231-8. The role of point-of-care ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion: a single academic center retrospective study. Ultrasound J. Crit Care Med.












Let's personalize your content