ECG Blog #448 — A Young Man with Chest Pain.
Ken Grauer, MD
SEPTEMBER 21, 2024
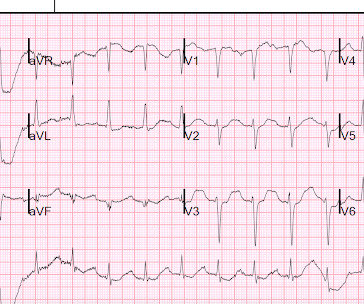
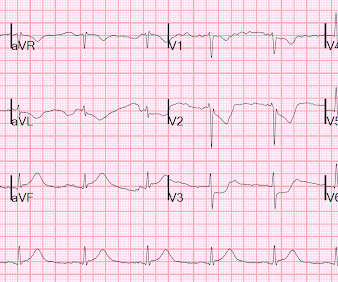
The ECG in Figure-1 was obtained from a previously healthy man in his early 20s — who initially presented with GI symptoms, that then evolved into CP ( C hest P ain ). QUESTIONS: Given the above history — How would YOU interpret the initial ECG that is shown in Figure-1 ? Figure-1: The initial ECG in today's case. (











Let's personalize your content