A man in his 60s with syncope and ST depression. What does the ECG mean?
Dr. Smith's ECG Blog
OCTOBER 25, 2023
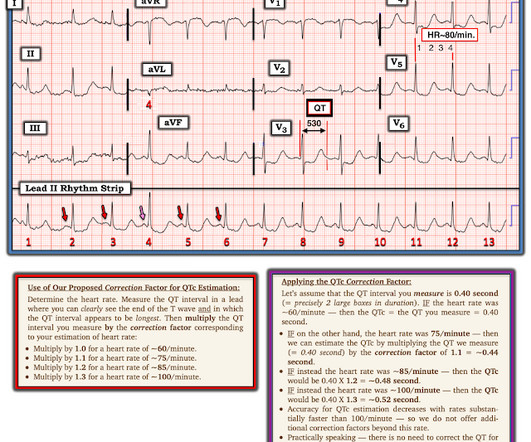
Here is his triage ECG: What do you think? What is the most likely cause of the patient’s ECG findings, and what would be your first step in management? What does the ECG show? What does the ECG show? Figure-1: The initial ECG in this case — and a rapid method for estimating the QTc ( See text ). Is it STEMI?











Let's personalize your content