A teenager involved in a motor vehicle collision with abnormal ECG
Dr. Smith's ECG Blog
FEBRUARY 6, 2024
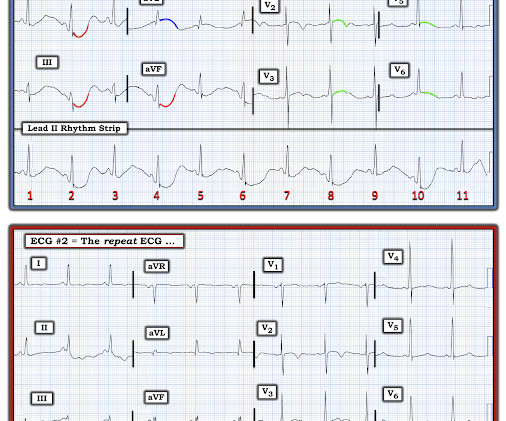
Here is his initial ECG around 1330: What do you think? The ECG shows sinus tachycardia with RBBB and LAFB, without clear additional superimposed signs of ischemia. Initial high sensitivity troponin I: 3,830 ng/L (URL 20 ng/L for men) 1445: Similar to initial ECG. He was intubated for altered mental status.



















Let's personalize your content