Hyperthermia and ST Elevation
Dr. Smith's ECG Blog
JANUARY 30, 2019
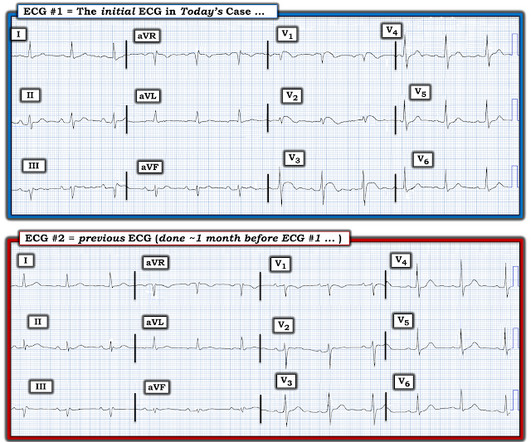
I remember Allie well from her days in the Research volunteer program at Hennepin. Smith comment: 1) Brugada ECG may have ST shifts in limb leads as well as precordial leads. A repeat EKG was performed at that time and showed this: The STE had almost completed resolved and the STE depression is improved as well. F (rectal).













Let's personalize your content